MHI Hydrogen Infrastructure Assists Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub with Funding, Technology
Node 6 will produce hydrogen via electrolysis and peak-power generation with 100% hydrogen-capable turbines.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Hydrogen Infrastructure (MHI H2I) signed an agreement with the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Association (PNWH2) and the Boardman Hydrogen Hub project to accelerate the region’s deploying clean hydrogen infrastructure and technologies. The agreement advances MHI H2I’s project development efforts and enables access to funding from the Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Clean Energy Demonstrations. Mitsubishi Power Americas will leverage its hydrogen technology and solutions for hub development and to satisfy the DOE’s clean-energy goals.
“This step solidifies our position in the PNWH2 Hub and underscores our commitment to advancing the hydrogen economy in the United States,” said Scott Neumeister, Director of Regional Business Development, MHI Hydrogen Infrastructure. “The Pacific Northwest is poised to serve as a national benchmark for successful low-carbon intensity and economically viable green hydrogen production. The development of hydrogen infrastructure at scale is critical, as is developing commercial frameworks for long-term services and support. While the challenges ahead are significant, they also present opportunities to collaborate across the industry. We look forward to continuing our efforts and working together toward a carbon-free energy future.”
Node 6
MHI H2I’s Node 6, in collaboration with Portland General Electric and Williams, will use hydrogen for dispatchable electricity generation. It will also deliver hydrogen to Node 3 for liquefaction and supply into the heavy-duty transportation sector. This node will produce hydrogen via electrolysis and peak power generation with 100% hydrogen-capable turbines. Node 6 infrastructure includes:
- Hydrogen pipeline to provide long-duration energy storage for the power plant
- Hydrogen delivery pipeline to Node 3, located approximately 20 miles from the production site
PNWH2 & H2Hubs
The PNWH2 Hub contains nodes across Washington, Oregon, and Montana, and is progressing through Phase 1 of the DOE’s H2Hubs Program. It uses regional technology and renewable energy to expand clean hydrogen across numerous markets, reducing carbon emissions in heavy-duty transportation, port operations, fertilizer and cement production, and power generation.
Nodes on PNWH2's Hub map; image credit: PNWH2
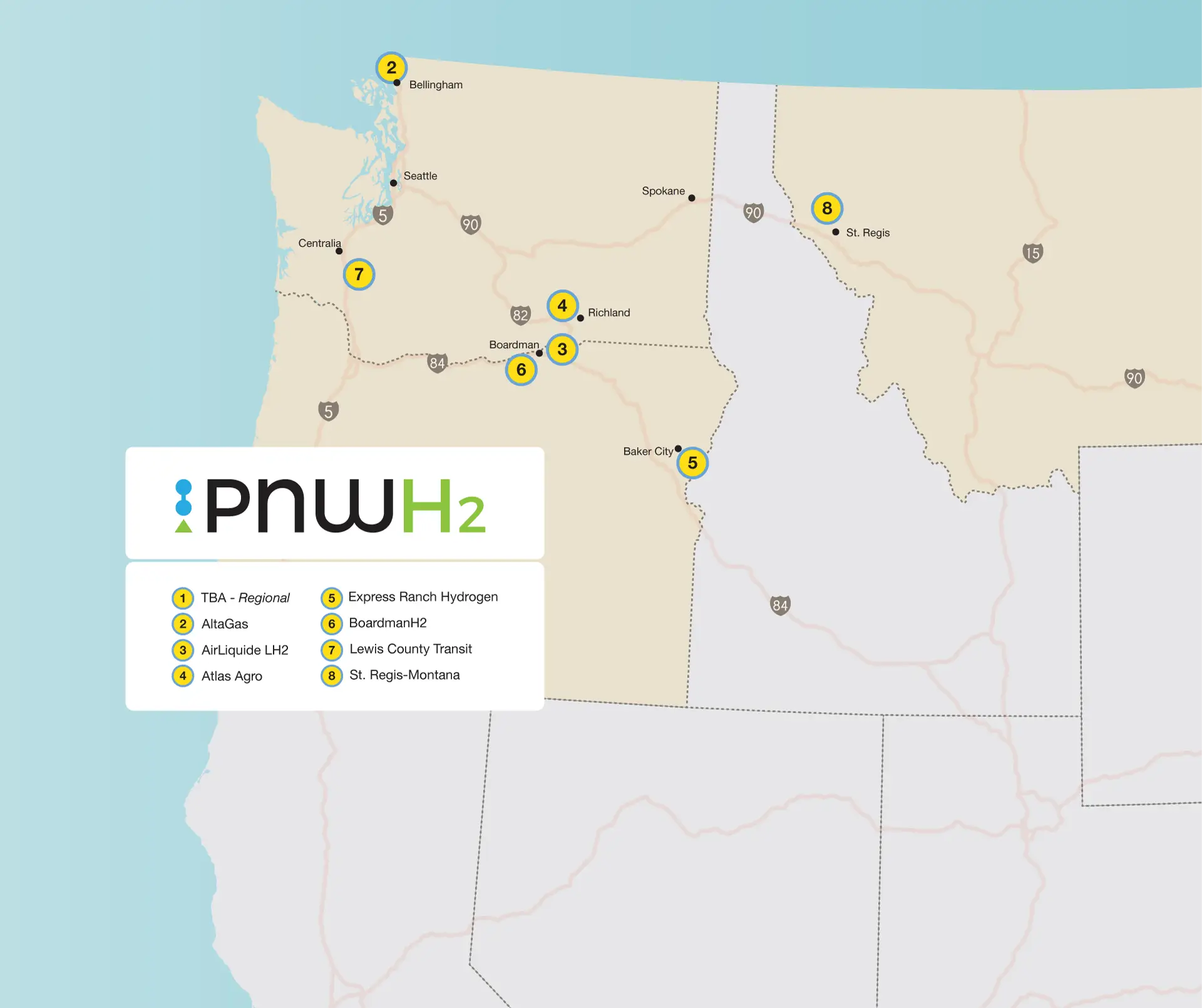
“Our group of partners form the backbone of PNWH2’s work to accelerate the investment in and deployment of clean hydrogen technologies,” said Chris Green, President of the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Association. “Formalizing our project subrecipient agreements marks a significant step in laying the groundwork for the Hub’s development, putting us on the path to achieving our goal of establishing the Pacific Northwest in bringing new energy manufacturing jobs to our region.”
The Regional Clean Hydrogen Hubs Program will build hubs across the country to accelerate a clean energy economy in the United States and, with funding from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, will kickstart a network of clean hydrogen producers, consumers, and connective infrastructure. The H2Hubs will also support the production, storage, delivery, and end-use of clean hydrogen.
DOE’s Hydrogen Work
In late July 2024, PNWH2 became one of the first U.S. Regional Clean Hydrogen Hubs to reach Phase 1 designation with the DOE’s recent award status. PNWH2 will receive up to $27.5 million of a potential $1 billion in future federal funding. Phase 1 includes initial planning, permitting, and analysis work to ensure the Hub concept’s technological and financial viability.
Washington State University’s Consortium for Hydrogen and Renewably Generated E-Fuels will oversee the Community Benefits Plan for the PNWH2 Hub, while project management is led by AtkinsRéalis US Nuclear.