MHI Thermal Systems Delivers Centrifugal Chillers to Emirati Cooling Plants
The Emirates Central Cooling Systems Corp. (Empower) will supply chilled water for cooling to residential, commercial, healthcare, educational, and multi-use projects.
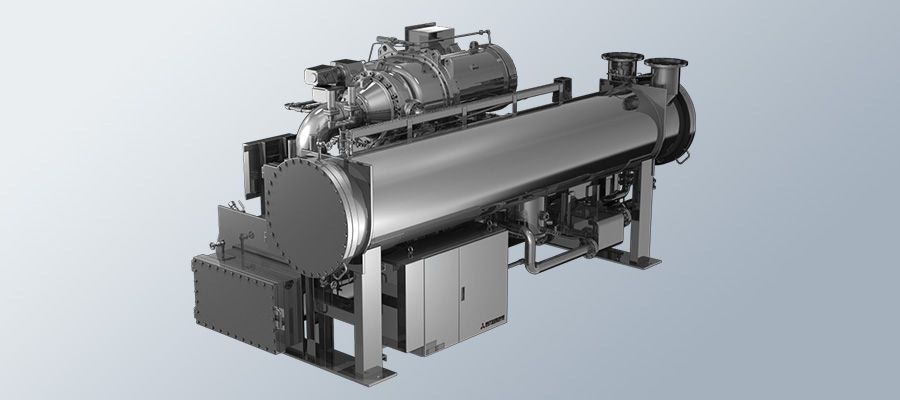
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Thermal Systems (MHI Thermal Systems) signed an agreement with Empower to supply large-scale centrifugal chillers for district cooling plants in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. Per the agreement, MHI Thermal Systems will deliver 18 advanced chillers, ready for delivery by 2025, with an aggregate cooling capacity of 56,250 refrigeration tons (RT).
"We are proud that Empower has evaluated the performance and the quality of the after-sales service of the units previously delivered and has once more chosen MHI Thermal Systems' chillers for these latest projects,” said Yoshihiro Ito, President of MHI Thermal Systems. “We will continue improving energy efficiency while continuously enhancing operational and production effectiveness. We will continue implementing our solutions to Empower's DCS plants so that our partnership will also contribute to the Dubai and the UAE's carbon emissions reduction strategy."
Empower will operate the chillers in three district cooling system plants, supplying chilled water for cooling to residential, commercial, healthcare, educational, and multi-use projects. The agreement also includes a provision enabling Empower to increase the order size, potentially raising the total capacity to 100,000 RT. Delivery will begin sequentially from 2025, bringing Empower’s total number of chillers to 46 units.
Centrifugal chiller; image credit: MHI Thermal Systems
News from MHI Group
In late August 2024, Mitsubishi Shipbuilding, Imabari Shipbuilding, Japan Marine United Corp. and Nihon Shipyard formed a joint study with a collection of shipping companies, including “K” Line, NYK Line, and MOL, to establish standard specifications and designs for liquefied CO2 (LCO2) carriers. The joint study also enables LCO2 carrier construction at additional shipyards in Japan.
The consortium will collaborate with industry stakeholders and shipyards, advancing Japanese decarbonization and construction supply chains by developing low-emission ships using low-carbon fuels, such as ammonia. The demand for LCO2 carriers is expected to grow alongside CCS projects that transport CO2 to storage sites by sea. Considering this market trend, the construction and supply of LCO2 carriers will strengthen the CCS value chain and improve economic efficiency.
Also in August, MHI signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with TFC to conduct a joint pre-feasibility study on establishing an ammonia value chain in Taiwan, supporting the country’s 2050 Net-Zero Emissions goal. MHI and TFC will explore facilities and economic feasibility of the fuel ammonia value chain, including ammonia receiving, storage, handling, and delivery to power plants. In addition, the MoU will assess using ammonia as a fuel for power generation. Ammonia, comprised of hydrogen and nitrogen, is an efficient carrier for hydrogen transportation and can undergo fuel combustion without emitting CO2.
Taiwan’s 2050 Net-Zero Emissions target focuses on cutting carbon emissions and integrating less carbon-intensive fuels. To support the initiative, TFC will use blue ammonia and green ammonia as fuel in Taiwan. In June 2023, TFC imported the country’s first low-carbon ammonia and, in January 2024, created an Ammonia Energy Division.
In June 2024, the Electricity Generating Authority of Thailand (EGAT) and MHI agreed to research the integration of hydrogen co-firing technologies in gas turbine-driven power generation facilities in Thailand. Backing the country’s goal of reaching carbon neutrality by 2050 and net-zero emissions by 2065, the partners’ research will facilitate the conversion of thermal power plants to clean-fuel operation.